Introduction
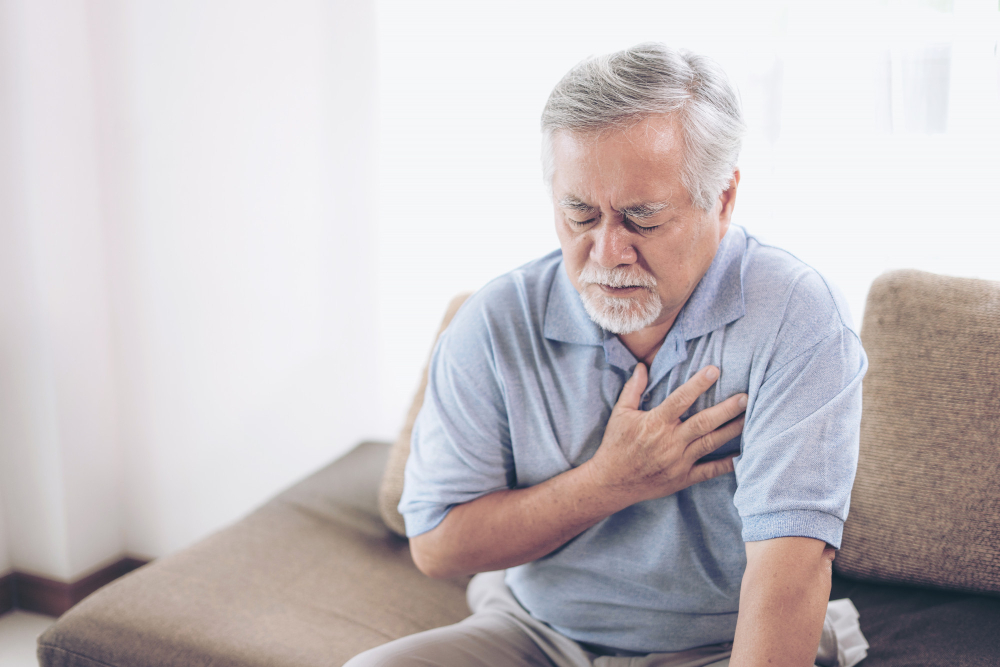
Understanding the difference between stable and unstable angina is important for your heart health. Angina is chest pain caused by reduced blood flow to the heart. Both stable and unstable angina are warning signs that your heart needs attention. Knowing angina symptoms, chest pain causes, and when to seek help can save lives. In this blog, we will explain stable vs unstable angina, their symptoms, and how to protect your heart.
What is Angina?
Angina is a type of chest pain. It happens when your heart does not get enough oxygen-rich blood. Usually, angina feels like pressure, squeezing, or tightness in the chest. Sometimes, the pain can spread to your arms, neck, jaw, or back. Angina is not a disease itself. Instead, it is a symptom of heart problems, often due to narrowed arteries. Angina can be a sign of coronary artery disease, which is a common heart condition.
What is Stable Angina?
Stable angina is the most common type of angina. It usually happens during physical activity or stress. For example, you may feel chest pain when walking fast or climbing stairs. The pain often goes away with rest or after taking medicine. Stable angina follows a pattern. You may notice it happens at certain times or after certain activities. The symptoms are usually mild and last a few minutes.
Symptoms of Stable Angina
Triggers and Risk Factors
What is Unstable Angina?
Unstable angina is more serious than stable angina. It can happen at any time, even when you are resting. The pain may be stronger, last longer, or come without warning. Unstable angina is a sign that your heart is at risk for a heart attack. Unlike stable angina, rest or medicine may not help. Because of this, unstable angina is a medical emergency.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
Risk Factors
Stable vs Unstable Angina: Main Differences
Diagnosis
If you have chest pain, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and health history. They may do tests to find the cause. Common tests include:
If your chest pain is new, severe, or different from before, see a doctor right away. Early diagnosis can prevent serious problems.
Treatment Options
Treatment for angina depends on the type and severity. For stable angina, doctors may suggest:
For unstable angina, you may need hospital care. Doctors may give stronger medicines, or perform procedures to open blocked arteries. Quick treatment can lower the risk of a heart attack.
Prevention Tips
There are steps you can take to lower your risk of angina and heart disease. For example:
These habits can help prevent angina attacks and improve your heart health.
When to Seek Immediate Medical Help
If you have chest pain that is new, severe, or does not go away with rest, seek help right away. Call emergency services if you notice:
Unstable angina can lead to a heart attack. Quick action can save your life.
Conclusion
“Knowing the difference between stable and unstable angina can help you protect your heart. If you experience chest pain or suspect angina, consult Dr. Pradheep K Rachakonda, a skilled cardiac surgeon, for personalized advice on heart health.”